Since September 2018, 360Netlab Scanmon has detected multiple scan spikes on TCP port 5431, each time the system logged more than 100k scan sources, a pretty large number compared with most other botnets we have covered before.
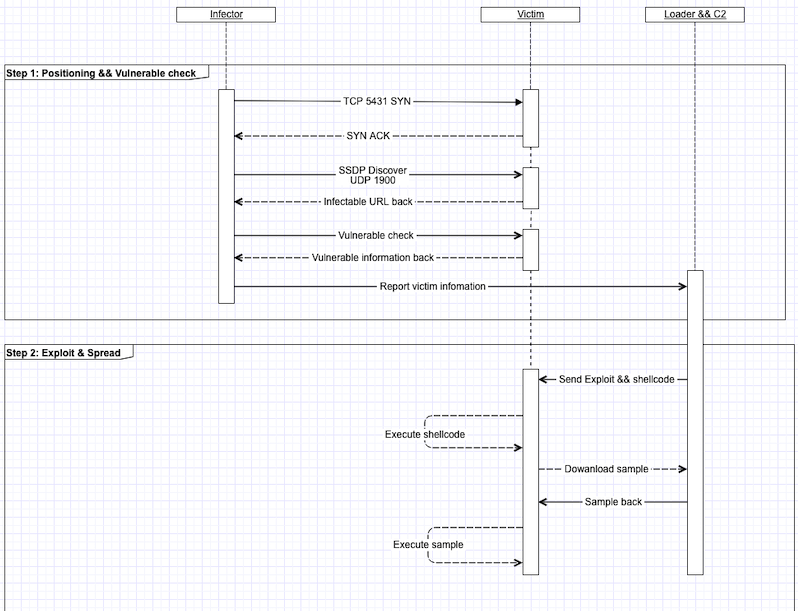
The interaction between the botnet and the potential target takes multiple steps, it starts with tcp port 5431 destination scan, then moving on to check target’s UDP port 1900 and wait for the target to send the proper vulnerable URL. After getting the proper URL, it takes another 4 packet exchanges for the attacker to figure out where the shellcode’s execution start address in memory is so a right exploit payload can be crafted and fed to the target.
At the beginning we were not able to capture a valid sample as the honeypot needs to be able to simulate the above scenarios. We had to tweak and customize our honeypot quite a few times, then finally in Oct, we got it right and successfully tricked the botnet to send us the sample (we call it BCMUPnP_Hunter).
The botnet has the following characteristics:
- The amount of infection is very large, the number of active scanning IP in each scan event is about 100,000;
- The target of infection is mainly router equipment with BroadCom UPnP feature enabled.
- Self-built proxy network (tcp-proxy), the proxy network is implemented by the attacker, the proxy currently communicates with well-known mail servers such as Outlook, Hotmail, Yahoo! Mail, etc. We highly suspect that the attacker’s intention is to send spams.
Scale Assessment
The trend of scanning source IP for TCP port 5431 in the last 30 days is as follows:
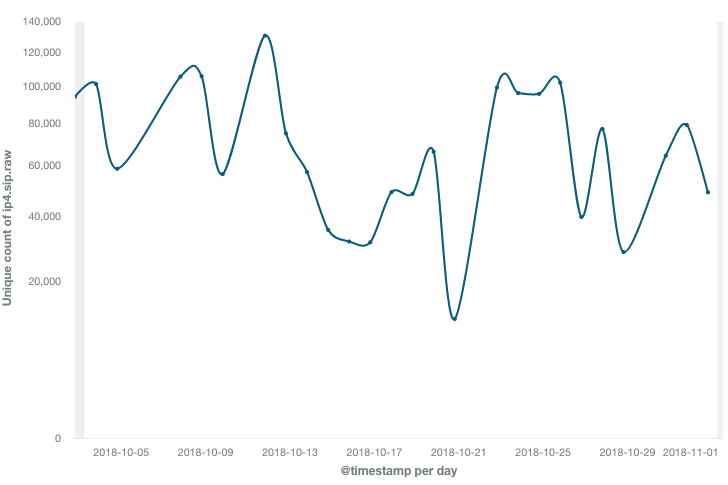
- It can be seen that the scan activity picks up every 1-3 days. The number of active scanning IP in each single event is about 100,000
- All together we have 3.37 million unique scan source IPs. It is a big number, but it is likely that the IPs of the same infected devices just changed over time.
- The number of potential infections may reach 400,000 according to Shodan based on the search of banner:
Server: Custom/1.0 UPnP/1.0 Proc/Ver
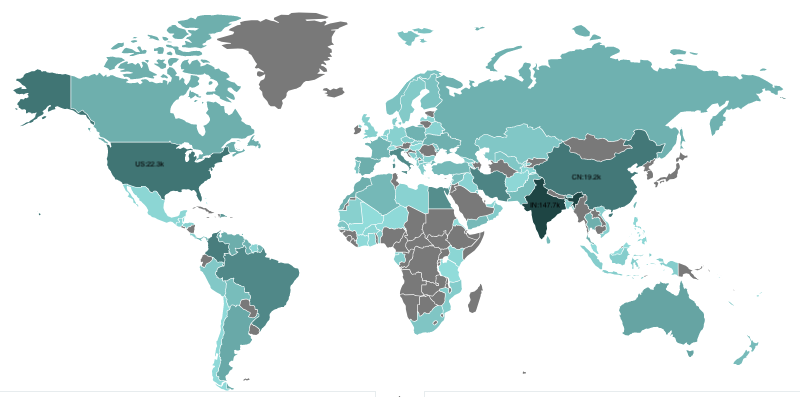
Geographical distribution for the scanner IPs in the last 7 days.
Infected Device Information
We probed the scanners, and 116 different type of infected device information is obtained, the actual infected device type should be more than what displays below:
ADB Broadband S.p.A, HomeStation ADSL Router
ADB Broadband, ADB ADSL Router
ADBB, ADB ADSL Router
ALSiTEC, Broadcom ADSL Router
ASB, ADSL Router
ASB, ChinaNet EPON Router
ASB, ChinaTelecom E8C(EPON) Gateway
Actiontec, Actiontec GT784WN
Actiontec, Verizon ADSL Router
BEC Technologies Inc., Broadcom ADSL Router
Best IT World India Pvt. Ltd., 150M Wireless-N ADSL2+ Router
Best IT World India Pvt. Ltd., iB-WRA300N
Billion Electric Co., Ltd., ADSL2+ Firewall Router
Billion Electric Co., Ltd., BiPAC 7800NXL
Billion, BiPAC 7700N
Billion, BiPAC 7700N R2
Binatone Telecommunication, Broadcom LAN Router
Broadcom, ADSL Router
Broadcom, ADSL2+ 11n WiFi CPE
Broadcom, Broadcom Router
Broadcom, Broadcom ADSL Router
Broadcom, D-Link DSL-2640B
Broadcom, D-link ADSL Router
Broadcom, DLink ADSL Router
ClearAccess, Broadcom ADSL Router
Comtrend, AR-5383n
Comtrend, Broadcom ADSL Router
Comtrend, Comtrend single-chip ADSL router
D-Link Corporation., D-Link DSL-2640B
D-Link Corporation., D-Link DSL-2641B
D-Link Corporation., D-Link DSL-2740B
D-Link Corporation., D-Link DSL-2750B
D-Link Corporation., D-LinkDSL-2640B
D-Link Corporation., D-LinkDSL-2641B
D-Link Corporation., D-LinkDSL-2741B
D-Link Corporation., DSL-2640B
D-Link, ADSL 4*FE 11n Router
D-Link, D-Link ADSL Router
D-Link, D-Link DSL-2640U
D-Link, D-Link DSL-2730B
D-Link, D-Link DSL-2730U
D-Link, D-Link DSL-2750B
D-Link, D-Link DSL-2750U
D-Link, D-Link DSL-6751
D-Link, D-Link DSL2750U
D-Link, D-Link Router
D-Link, D-link ADSL Router
D-Link, DVA-G3672B-LTT Networks ADSL Router
DARE, Dare router
DLink, D-Link DSL-2730B
DLink, D-Link VDSL Router
DLink, DLink ADSL Router
DQ Technology, Inc., ADSL2+ 11n WiFi CPE
DQ Technology, Inc., Broadcom ADSL Router
DSL, ADSL Router
DareGlobal, D-Link ADSL Router
Digicom S.p.A., ADSL Wireless Modem/Router
Digicom S.p.A., RAW300C-T03
Dlink, D-Link DSL-225
Eltex, Broadcom ADSL Router
FiberHome, Broadcom ADSL Router
GWD, ChinaTelecom E8C(EPON) Gateway
Genew, Broadcom ADSL Router
INTEX, W150D
INTEX, W300D
INTEX, Wireless N 150 ADSL2+ Modem Router
INTEX, Wireless N 300 ADSL2+ Modem Router
ITI Ltd., ITI Ltd.ADSL2Plus Modem/Router
Inteno, Broadcom ADSL Router
Intercross, Broadcom ADSL Router
IskraTEL, Broadcom ADSL Router
Kasda, Broadcom ADSL Router
Link-One, Modem Roteador Wireless N ADSL2+ 150 Mbps
Linksys, Cisco X1000
Linksys, Cisco X3500
NB, DSL-2740B
NetComm Wireless Limited, NetComm ADSL2+ Wireless Router
NetComm, NetComm ADSL2+ Wireless Router
NetComm, NetComm WiFi Data and VoIP Gateway
OPTICOM, DSLink 279
Opticom, DSLink 485
Orcon, Genius
QTECH, QTECH
Raisecom, Broadcom ADSL Router
Ramptel, 300Mbps ADSL Wireless-N Router
Router, ADSL2+ Router
SCTY, TYKH PON Router
Star-Net, Broadcom ADSL Router
Starbridge Networks, Broadcom ADSL Router
TP-LINK Technologies Co., Ltd, 300Mbps Wireless N ADSL2+ Modem Router
TP-LINK Technologies Co., Ltd, 300Mbps Wireless N USB ADSL2+ Modem Router
TP-LINK, TP-LINK Wireless ADSL2+ Modem Router
TP-LINK, TP-LINK Wireless ADSL2+ Router
Technicolor, CenturyLink TR-064 v4.0
Tenda, Tenda ADSL2+ WIFI MODEM
Tenda, Tenda ADSL2+ WIFI Router
Tenda, Tenda Gateway
Tenda/Imex, ADSL2+ WIFI-MODEM WITH 3G/4G USB PORT
Tenda/Imex, ADSL2+ WIFI-MODEM WITH EVO SUPPORT
UTStarcom Inc., UTStarcom ADSL2+ Modem Router
UTStarcom Inc., UTStarcom ADSL2+ Modem/Wireless Router
UniqueNet Solutions, WLAN N300 ADSL2+ Modem Router
ZTE, Broadcom ADSL Router
ZTE, ONU Router
ZYXEL, ZyXEL VDSL Router
Zhone, Broadcom ADSL Router
Zhone, Zhone Wireless Gateway
Zoom, Zoom Adsl Modem/Router
ZyXEL, CenturyLink UPnP v1.0
ZyXEL, P-660HN-51
ZyXEL, ZyXEL xDSL Router
huaqin, HGU210 v3 Router
iBall Baton, iBall Baton 150M Wireless-N ADSL2+ Router
iiNet Limited, BudiiLite
iiNet, BoB2
iiNet, BoBLite
Botnet Workflow
As mentioned in the beginning, the bot has to go through multiple steps to infect a protentional target, see the following diagram for the workflow, note the Loader is ( 109.248.9.17:4369)
The Sample
The sample of the botnet consists of two parts, the shellcode and the Main sample, which are described below.
shellcode
The main function of shellcode is to download the main sample from C2(109.248.9.17:8738) and execute it.
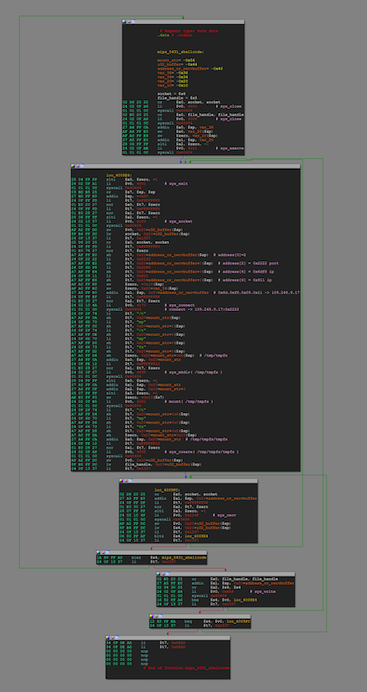
The shellcode has a full length of 432 bytes, very neatly organized and written, some proofs below (We did not find similar code using search engines). It seems that the author has profound skills and is not a typical script kid:
- Code basic: The code has multiple syscall calls for networks, processes, files, etc.
- Some details:
syscall 0x40404(instead ofsyscall 0) and multiple inversion operations were used so bad characters (\x00) could be avoided; the stack variables in the code also have different degrees of multiplexing to optimize the runtime stack structure; - Code logic: by calling the Loop at various section, the possibility of many failed calls is reasonably avoided, and the validity of shellcode execution is guaranteed.
The complete flow chart is as follows:
Main Sample
The main sample includes BroadCom UPnP vulnerability probe and a proxy access network module, it can parse four instruction codes from C2:
Command Code | Length | Function
0x00000000 0x18 The first packet, no practical function
0x01010101 0x4c Search for potential vulnerable target
0x02020202 0x08 Empty current task
0x03030303 0x108 Access Proxy Network
0x01010101to enable the port scan task, once the BOT IDs a potential target, the target IP will be reported to the Loader, and then the Loader will complete the subsequent infection process.0x03030303is for the proxy service, BOT accesses the address provided in the instruction and reports the access result to the C2. This can generate real economic benefits. Attackers can use this command to build a proxy network, and then profit from doing things such as sending spam, simulating clicks, and so on.
Proxy Network and Spam
In the instructions we have obtained, BCMUPnP_Hunter is used to proxy traffic to the following servers:
104.47.0.33:25
104.47.12.33:25
104.47.124.33:25
104.47.14.33:25
104.47.33.33:25
104.47.48.33:25
104.47.50.33:25
106.10.248.84:25
144.160.159.21:25
188.125.73.87:25
67.195.229.59:25
74.6.137.63:25
74.6.137.64:25
98.137.159.28:25
This table shows what we have dug out from our various data sources for the above IPs:
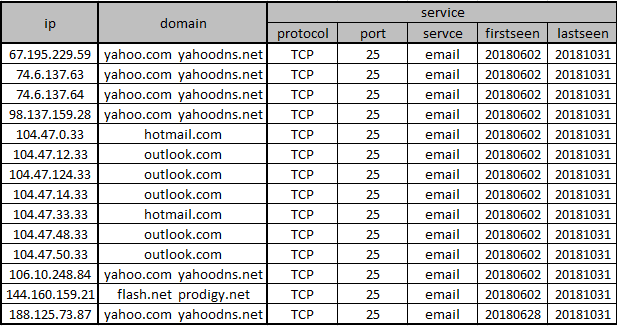
As can be seen:
- These servers are all well-known mail service providers, including Outlook, Hotmail, Yahoo! Mail;
- For several months, these servers have provided and only provided TCP25 services;
- In this case, it appears that the attacker is abusing the email service of these servers;
This makes us highly skeptical that the attacker is using the proxy network established by BCMUPnP_Hunter to send spam.
To read the original article:
https://blog.netlab.360.com/bcmpupnp_hunter-a-100k-botnet-turns-home-routers-to-email-spammers-en/