All these vulnerabilities lie in the secure part of the AMD’s Zen architecture processors and chipsets—typically where device stores sensitive information such as passwords and encryption keys and makes sure nothing malicious is running when you start your PC.
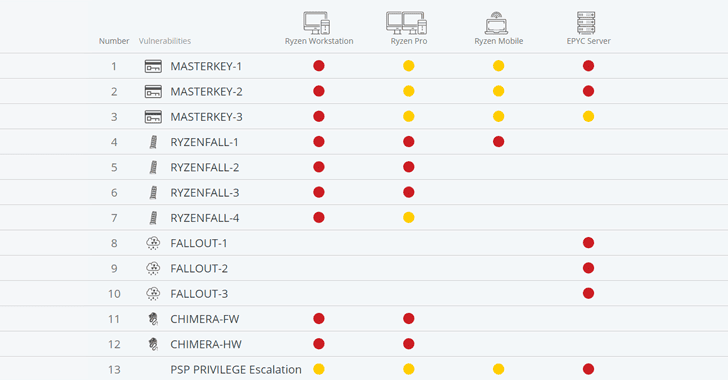
The unpatched vulnerabilities are categorized into four classes—RYZENFALL, FALLOUT, CHIMERA, and MASTERKEY—and threaten wide-range of servers, workstations, and laptops running vulnerable AMD Ryzen, Ryzen Pro, Ryzen Mobile or EPYC processors.
Moreover, researchers also found two exploitable manufacturer backdoors inside Ryzen chipset that could allow attackers to inject malicious code inside the chip.
AMD’s Ryzen chipsets are found in desktop and laptop computers, while EPYC processors in servers. Researchers successfully tested the vulnerabilities in 21 different products and believed 11 more products are also vulnerable to the issues.
Here’s the brief explanation of all the vulnerabilities:
RYZENFALL (v1, v2, v3, v4) AMD Vulnerabilities
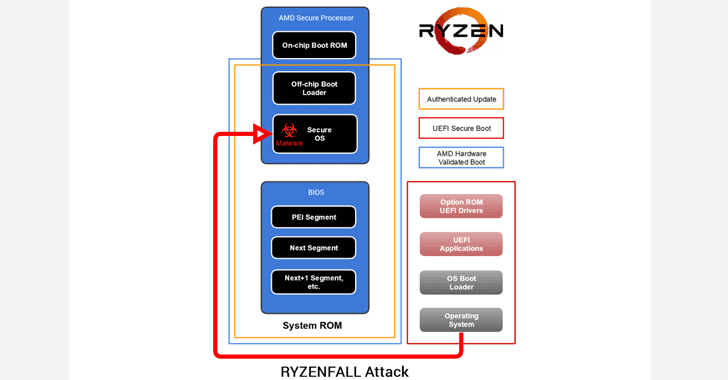
These flaws reside in AMD Secure OS and affect Ryzen secure processors (workstation/pro/mobile).
According to researchers, RYZENFALL vulnerabilities allow unauthorized code execution on the Ryzen Secure Processor, eventually letting attackers access protected memory regions, inject malware into the processor itself, and disable SMM protections against unauthorized BIOS reflashing.
Attackers could also use RYZENFALL to bypass Windows Credential Guard and steal network credentials, and then use the stolen data to spread across to other computers within that network (even highly secure Windows corporate networks).
RYZENFALL can also be combined with another issue called MASTERKEY (detailed below) to install persistent malware on the Secure Processor, « exposing customers to the risk of covert and long-term industrial espionage. »
FALLOUT (v1, v2, v3) AMD Vulnerabilities
These vulnerabilities reside in the bootloader component of EPYC secure processor and allow attackers to read from and write to protected memory areas, such as SMRAM and Windows Credential Guard isolated memory.
FALLOUT attacks only affect servers using AMD’s EPYC secure processors and could be exploited to inject persistent malware into VTL1, where the Secure Kernel and Isolated User Mode (IUM) execute code.
To read the original article: